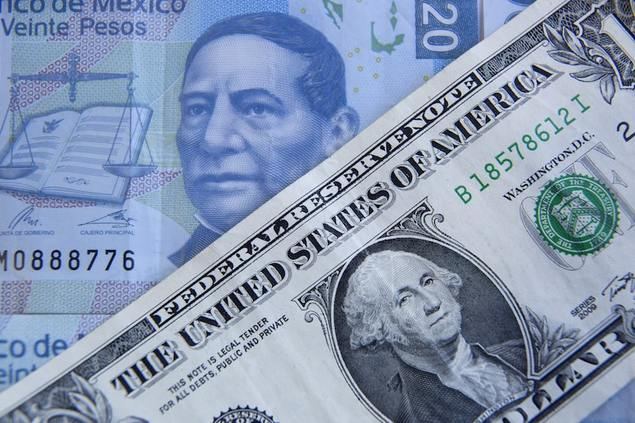
The Mexican government has attempted to prevent the imposition of these tariffs through intense negotiations in the United States. However, Donald Trump's administration confirmed that the measures will take effect on March 4. This situation has created an atmosphere of uncertainty among investors, who have begun making more cautious decisions in their transactions with the Mexican peso. The potential prolongation of these trade tensions could adversely affect foreign direct investment and the country's economic growth.
One of the immediate effects of this volatility has been an increase in demand for safe-haven assets such as the U.S. dollar and gold. The peso's depreciation also impacts stock markets and the confidence of foreign investors, who are assessing the risks of continuing operations in Mexico amid a more protectionist trade environment. Mexican exports could be affected, particularly in key sectors such as automotive and manufacturing, which heavily rely on trade with the United States.
On the other hand, China has responded firmly to the new tariffs imposed by Trump, warning of possible economic retaliation. The escalation of trade tensions between the world's largest economies has contributed to increased global volatility and has affected risk perception in emerging markets such as Mexico. While Mexico is not a primary actor in the U.S.-China dispute, global uncertainty indirectly impacts the country, affecting trade and investment.
Mexico has intensified its cooperation efforts to improve diplomatic relations with the United States and mitigate the impact of the sanctions. Recently, the Mexican government extradited 29 high-profile drug traffickers to U.S. territory, a move that some analysts interpret as a strategy to seek relief from trade tensions. Additionally, proposals have been made to diversify export markets, strengthening trade relations with Europe, Asia, and Latin America to reduce dependence on the United States.
Despite these efforts, the outlook remains uncertain. U.S. trade policy has proven unpredictable and highly volatile, making economic and financial planning in Mexico more difficult. The coming days will be crucial in determining whether the peso stabilizes or continues under pressure in international markets. Furthermore, the Bank of Mexico may intervene with monetary policy adjustments to contain volatility and prevent an inflationary impact on the national economy.
In conclusion, the depreciation of the Mexican peso reflects the uncertainty generated by trade tensions with the United States. Implementing new tariffs represents a significant challenge for the Mexican economy, which seeks to maintain its competitiveness in a changing global environment. The response of Mexican authorities will be crucial for exchange rate stability and investor confidence in the country. In the long term, Mexico must strengthen its trade diversification strategy and bolster its domestic economy to face similar scenarios in the future.







 Si (
Si ( No(
No(

















